近日,福建海洋可持续发展研究院(厦门大学)张增凯教授团队联合国内多家研究单位,编制了中国沿海省份海洋经济投入产出表,为我国海洋经济与管理领域研究提供了一套开源数据集,在海洋社会经济与自然生态复合系统研究领域具有应用潜力。该研究进展以 “Ocean economic input-output tables of coastal provinces in China” 为题,发表在Scientific Data上。
海洋经济是指开发、利用和保护海洋的各类产业活动,以及与之相关联活动的总和。海洋经济已成为我国国家发展、世界经济格局重构及全球挑战应对等方面的战略新高地,也是国际竞争的焦点。党的二十大明确提出,发展海洋经济,保护海洋生态环境,加快建设海洋强国。海洋经济正成为我国国民经济发展的新引擎,对沿海省份经济增长的拉动作用尤为显著。2023年,全国海洋生产总值达9.9万亿元,占国内生产总值的7.9%。
列昂惕夫在1936年提出投入产出分析模型,为研究社会生产各部门之间的相互依赖关系,特别是系统地分析经济内部各产业之间错综复杂的交易提供了一种实用的经济分析方法。投入产出模型被引入中国之后,在分析我国经济现实问题中得到了广泛应用,也为我国不同时期经济决策提供了重要参考。投入产出表是投入产出模型的数据基础,是反映一定时期各部门间相互联系和平衡比例关系的一种平衡表。但是,统计部门发布的投入产出表仍然采用传统的经济部门分类,难以捕捉海洋和陆域部门的异质性,这给全面细致地分析海洋经济带来了挑战。
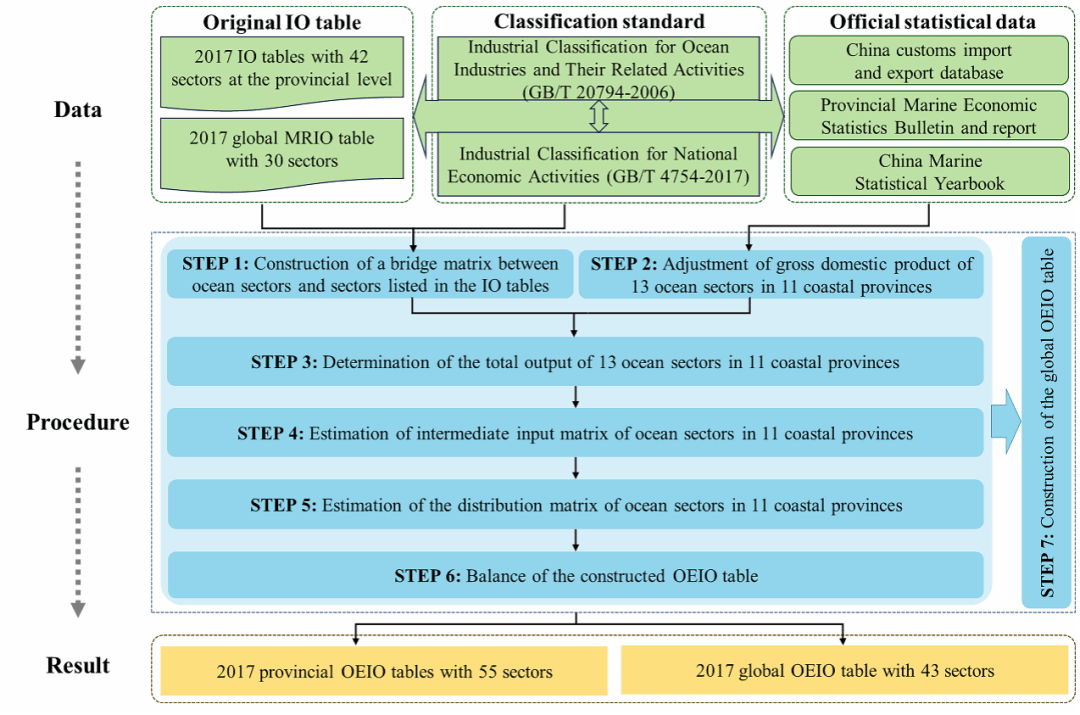
研究团队基于相关沿海省份统计局公布的2017年省级投入产出表和海洋经济统计数据,构建了涵盖中国 11 个沿海省份及其13个海洋部门的海洋经济投入产出表:首先,依据《海洋及相关产业分类》(GB/T 20794-2006)和《国民经济行业分类》(GB/T 4754-2017),通过构建桥矩阵将 13 个海洋部门与省级投入产出表中 42 个传统部门进行匹配。其次,收集整理了海洋经济在省级和部门级的国内生产总值数据,并通过数据调平获得相应部门的增加值。在此基础上,估算海洋产业的总产出及其相应的剥离系数,进而利用剥离系数从官方投入产出表的对应传统部门中拆分出海洋部门的中间投入矩阵和分配矩阵,并对省级海洋经济投入产出表进行调平。最后,基于该方法构建了包含中国沿海省份海洋产业的全球投入产出表。
该开源数据在海洋经济核算、海洋产业关联分析、海洋经济活动的环境生态影响评估等领域具有一定的应用潜力,可以为海洋经济评估与管理政策制定提供有力支撑。
该论文的共同第一作者为厦门大学2023级硕士生梁晓盈和博士生郑传增,通讯作者为张增凯教授,共同通讯作者还包括中国人民大学祝坤福教授、国家海洋信息中心和天津大学郑莉副研究员。该研究获得国家自然科学基金面上项目(72474188)、重大项目(72394404)以及香港特别行政区研究资助局项目(AoE/P-601/23-N)的联合资助。
Liang, X., Zheng, C., Zheng, L. et al. 2025. Ocean economic input-output tables of coastal provinces in China. Sci Data 12, 876. doi:10.1038/s41597-025-05221-3
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-025-05221-3https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.27959550
A research team led by Prof. Zhang Zengkai from FISO, in collaboration with multiple domestic research institutions, compiled an ocean economic input-output (IO) table for China's coastal provinces. This work provides an open-access dataset for studies in the field of marine economy and management in China, with potential applications in integrated socio-economic and natural ecological systems research related to the ocean. The research progress was published in Scientific Data under the title "Ocean Economic Input-Output Tables of Coastal Provinces in China."
Research Background
The ocean economy refers to the totality of ocean and ocean-related industrial activities that aim for the development, utilization and protection of the ocean. Many coastal countries have prioritized the development of their ocean economies as a fundamental strategy, positioning ocean sectors as the convergence zone for both international competition and cooperation. The ocean economy is serving as a new engine for China's economic development, with a particularly prominent impact on the economic growth of Chinese coastal provinces. In 2023, China's gross ocean product (GOP) reached 9.9 trillion yuan, accounting for 7.9% of the country's GDP.
In 1936, Wassily Leontief proposed the input-output analysis model, which provided a practical economic methodology for studying interdependencies among sectors of social production, particularly for systematically analyzing intricate economic transactions between industries. After its introduction to China, the input-output model has been extensively applied in analyzing the country's economic realities and has served as a crucial reference for economic decision-making across different periods. The input-output table, serving as the data foundation of this model, is essentially a balanced accounting framework that reflects inter-sectoral linkages and proportional equilibrium relationships during a given period. However, the input-output tables published by statistical authorities still adhere to traditional sectoral classifications, making it difficult to capture the heterogeneity between marine and terrestrial sectors, a limitation that poses significant challenges for conducting comprehensive and nuanced analyses of the marine economy.
Research Results
We constructed the OEIO datasets of China's coastal province in 2017, based on the official provincial IO tables published by the National Bureau of Statistics and the global MRIO table published by OECD that contains Chinese provinces. The processes of separating the characteristics of the ocean economy entail seven key steps: (1) We constructed a bridge matrix linking 13 ocean sectors with 42 sectors listed in the provincial IO tables based on Industrial Classification for Ocean Industries and Their Related Activities (GB/T 20794-2006) and Industrial Classification for National Economic Activities (GB/T 4754-2017). (2) We collected the gross domestic product of ocean economy at the sectoral and provincial level respectively, and adjusted the data to maintain consistency in total values. (3) We estimated the total outputs of ocean sectors in coastal provinces based on the gross domestic product and value-added rates derived from micro-level enterprise data. (4) We estimated the intermediate input matrix of ocean sectors based on the stripping coefficients, which are calculated as the ratio of the output of ocean sectors to the output of corresponding sectors in the official IO tables. (5) We estimated the distribution matrix of ocean sectors in coastal provinces based on the stripping coefficients calculated in the previous step. (6) We adopted the RAS method to balance the constructed provincial OEIO tables. (7) We repeated the above steps to differentiate the Chinese ocean sectors in a global MRIO table that contains Chinese provinces.
This open-source dataset offers significant analytical potential for marine economic accounting systems, inter-sectoral linkage analysis in marine industries, environmental impact assessments of marine economic activities etc., providing robust support for marine economy evaluation and management policy formulation.
The full text of this research is available at:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-025-05221-3
The dataset is available for download at:
https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.27959550


